COM iMX25 Bootloader U-Boot: Difference between revisions
From Wiki-DB
Jump to navigationJump to search
Ageisreiter (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Ageisreiter (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== Changelog == | == Changelog == | ||
[[COM iMX25 Bootloader Changelog|Changelog Files]] | |||
== Downloads == | == Downloads == | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 17 February 2012
FAQ
- Q: Update from U-Boot V1.11.2.0 to V1.14.0.0?
- A: Follow the six steps:
- Copy U-Boot binary (V1.14.0.0) to MicroSD Card
- Insert MicroSD Card to core module and connect DHCOM UART1 to host PC
- Start core module and enter bootloader console by pressing "enter" during start
- Call the command "nand erase c0000 bffff" and press enter
- Call the command "update bootloader" and press enter
- Restart the core module. The bootloader is updated now.
- Q: Update from U-Boot V1.5.0.0 or V1.7.0.0 to V1.14.0.0?
- A: Follow the sixsteps:
- Copy U-Boot binary (V1.14.0.0), splash bitmap, new settings binary and DHupdate.ini file to MicroSD Card
- DHupdate.ini file [update] content:
- splash *.bmp
- settings *.bin
- DHupdate.ini file [update] content:
- Insert MicroSD Card to core module and connect DHCOM UART1 to host PC
- Start core module and enter bootloader console by pressing "enter" during start
- Call the command "nand erase 80000 3ffff" and press enter
- Call the command "update bootloader u-boot.bin" and press enter
- After Update restart the core module and wait until bootloader has updateted splashimage and settings block (to prevent update repetition delete the update files from MicroSD Card after a successful update)
- Note: It is neccessary to flash the OS image again, if OS image was already flashed before bootloader update.
- Copy U-Boot binary (V1.14.0.0), splash bitmap, new settings binary and DHupdate.ini file to MicroSD Card
Changelog
Downloads
- Bootloader Binary
- Download U-Boot binary (v1.14.0.0) (for updating, please have a look at FAQ list)
- Settings Files
- DHupdate.ini example
- Update Bitmap example files
- Splash Image examples
Enter Bootloader Console
- Connect DHCOM UART1 via null modem cable to the Host PC
- Start terminal program (e.g. Tera Term) on the Host PC with the following settings:
- Baud rate: 38400
- Data: 8 bit
- Parity: none
- Stop bits: 1 bit
- Flow control: none
- Press "enter" on the Host PC during Core Module system start to enter bootloader console
Console commands
NAND Flash
- Nand Flash Read
- nand read <SDRAM address> <NAND Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example: nand read 80000000 400000 b40000
- Description: Copies 11,25MByte from NAND Flash address 0x40_0000 to SDRAM address 0x8000_0000
- Nand Flash Erase
- nand erase <Block base address> <Bytes>
- Example: nand erase 400000 40000
- Description: Deletes NAND Flash content from address 0x40_0000 to 0x43_FFFF
- Note: The Bytes information needs to be block size aligned!
- Nand Flash Write
- nand write <SDRAM address> <NAND Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example: nand write 80000000 400000 b40000
- Description: Cpoies 11,25MByte from SDRAM address 0x8000_0000 to NAND Flash address 0x40_0000
- Note: The Bytes information needs to be page size aligned!
- Show bad NAND Flash blocks
- nand bad
- Description: Shows the bad NAND Flash blocks.
- Show NAND FLash content
- nand dump <NAND Flash address>
- Example: nand dump 400000
- Description: Shows the content of the specified NAND Flash block
SPI Flash
- SPI Flash Init
- sf probe <bus:cs> [frequency]
- Example: sf probe 0:1
- Description: Initializes the OnBoard SPI Flash
- SPI Flash Read
- sf read <SDRAM address> <SPI Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example: sf read 80000000 40000 10000
- Description: Copies 64kByte from SPI Flash address 0x4_0000 to SDRAM address 0x8000_0000
- SPI Flash Write
- sf write <SDRAM address> <SPI Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example: sf write 80000000 40000 10000
- Description: Copies 64kByte from SDRAM address 0x8000_0000 to SPI Flash address 0x4_0000
- SPI Flash Erase
- sf erase <SPI Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example: sf erase 40000 10000
- Description: Deletes SPI Flash content from address 0x4_0000 to 0x4_FFFF
- Note: The Bytes information needs to be sector size aligned!
LCD contoller
- Show LCD controller settings
- lcdinfo
- Example:
Display Resolution: 800 x 480 pixels Display Type: Active Color Display Pixel Clock: 22 MHz Bits per Pixel: 16 Bits/Pixel Pixel Polarity: Active High VSYNC Polarity: Active Low HSYNC Polarity: Active Low Clock Polarity: Pos. Edge Output En Polarity: Active High HSYNC Puls Width: 64 Clock Cycles HSYNC Back Porch: 86 Clock Cycles HSYNC Front Porch: 42 Clock Cycles VSYNC Puls Width: 2 Line Cycles VSYNC Back Porch: 33 Line Cycles VSYNC Front Porch: 10 Line Cycles
GPIO's
- Show DHCOM GPIO settings
- gpioinfo
- Example:
GPIO_A: Direction = Input
State = 0
GPIO_B: Direction = Input
State = 0
GPIO_C: Direction = Input
State = 0
GPIO_D: Direction = Input
State = 0
GPIO_E: Direction = Input
State = 1
GPIO_F: Direction = Input
State = 1
GPIO_G: Direction = Output
State = 1
GPIO_H: Direction = Input
State = 1
GPIO_I: Direction = Input
State = 1
GPIO_J: Direction = Input
State = 1
GPIO_K: Direction = Input
State = 0
SD/MMC Card
- Switch between MicroSD and SD Slot
- mmcswitch <Slot number>
- Example: mmcswitch 2
- Description: Switch between SD/MMC Slots: 1 --> SD/MMC Slot, 2 --> MicroSD Slot
- Initialize SD/MMC Card
- mmcinit
- Description: Initialize new inserted SD Card
Filesystem
- Show Filesystem information
- fatinfo <interface> <device>
- Example: fatinfo mmc 1
Interface: MMC
Device 1: Vendor: Man 094150 Snr 266e068c Rev: 1.0 Prod: AF UD
Type: Removable Hard Disk
Capacity: 121.2 MB = 0.1 GB (248320 x 512)
Partition 1: Filesystem: FAT16 "NO NAME "
- List files
- fatls <interface> <device> <directory>
- Example 1: fatls mmc 1
- Example 2: fatls mmc 1 /folder
- Load Files from SD Card to SDRAM
- fatload <interface> <device> <SDRAM address> <directory+filename>
- Example 1: fatload mmc 1 80100000 nk.gz
- Example 2: fatload mmc 1 80100000 /folder/nk.gz
Ethernet
- Load File via TFTP to SDRAM
- tftp <SDRAM address> <directory+filename>
- Example: tftp 80100000 nk.gz
- Example TFTP Server: "Winagents TFTP Server Manager"
- Note: For TFTP download it is necessary to config the ENV variables "ipaddr" and "serverip"
- Ping
- ping <IP address>
- Example: ping 192.168.55.32
- Read PHY register via MII interface
- mii dump <PHY address> <PHY register>
- Example: mii dump 1 0
- Description: Shows PHY control register content.
Environment
- Show ENV variables
- printenv
bootdelay=0 baudrate=38400 ipaddr=192.168.55.230 serverip=192.168.55.36 gatewayip=192.168.55.36 netmask=255.255.255.0 frias=5 kernel=uImage bootargs=console=ttymxc0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 nandbootwince=update;bootwince 00200000 splashimage=0x000c0000 save_ENV_to_flash=setenv ENVinFlash 1; saveenv ENVinFlash=1 ethaddr=00:04:a3:34:b6:0d ethact=FEC0 winceimagetype=nk.gz winceimagesize=00ba55ee loadaddr=00200000 bootcmd=run nandbootwince filesize=212050 Environment size: 449/262140 bytes
- Set ENV variables
- setenv <ENV name> <ENV value>
- Example: setenv ipaddr 192.168.55.2
- Note: If you need to edit "bootcmd" it is necessary to insert ";" between the unique commands. You can enter ";" at the command line with "\;".
- Save ENV variables
- saveenv
- Erase all ENV variables
- eraseenv
- Note: It is necessary to restart the system after "eraseenv", to restore the default ENV settings.
Update
- Note: See also Bootloader subitem Flash Update.
- iMX25_update.bmp file
- update
- Description: Starts Flash update with "iMX25_update.bmp" file.
- Command line
- update <type> [filename]
- Type:
- wince = WinCE image update (default file names nk.gz or nk.bin) + ENV update
- linux = Linux image update (default file name uImage) + ENV update (default script file name uImage.env)
- flash = Complete flash image update
- bootloader = Bootloader update (default file name u-boot.bin)
- splash = Bootbitmap update (default file name splash.bmp)
- settings = Settings block update (default file name settings.bin)
I2C
- List available devices
- i2c probe
Valid chip addresses: 00 57 6F 0x5F = DHCOM i.MX25 Core Module EEPROM 0x6F = DHCOM i.MX25 Core Module Real Time Clock
- Read
- i2c md <I2C address> <I2C register> <Bytes>
- Example: i2c md 57 0 10
- Description: Reads 10 Bytes from the offset 0.
- Write
- i2c mw <I2C address> <I2C register> <Value> <Bytes>
- Example: i2c mw 57 0 aa 5
- Description: Writes 0xaa to 5 Bytes from the offset 0.
OS Boot
- WinCE
- bootwince <Image address> [debug]
- Example: bootwince 200000
- Description: The address 0x20_0000 specifies NAND Flash image address. The image is loaded from NAND flash to SDRAM. Next to that u-boot starts WinCE. The "debug" option make sure that the image wouldn't be started after uncompressing.
- Note: The Image address could also be an SDRAM address. But it is necessary to copy the Image (via tftp or nand flash commands) to the SDRAM before calling "bootwince".
- bootwince tftp
- Note: The ENV variables "loadaddr" and "bootfile" needs to be set before calling the command. For *.gz image types the "loadaddr" should be set to 0x8290_0000 and for *.bin images the address should be 0x8100_0000.
- Linux
- bootm <Kernel address> [arg]
- Note: When booting a Linux kernel,‘arg' can be the address of an initrd image.
Unzip
- unzip <source address> <destination address>
- Example: unzip 82900000 80100000
- Note: The unzip command is supporting the gzip file format.
Bitmap
- Information
- bmp info <Bitmap address>
Image size : 800 x 480 Bits per pixel: 8 Compression : 0
- Display
- bmp display <Bitmap SDRAM address> [x y]
Memory
- Display
- md[.b, .w, .l] <address> [count]
- Example: md.b 80100000 100
- Write
- mw[.b, .w, .l] <address> <value> [count]
- Example: mw.b 80100000 aa 100
- Description: Writes the value 0xaa to the next 0x100 bytes from the address 0x8010_0000.
- Copy
- cp[.b, .w, .l] <source> <destination> <count>
Show DHCOM Settings
- settings
- Example:
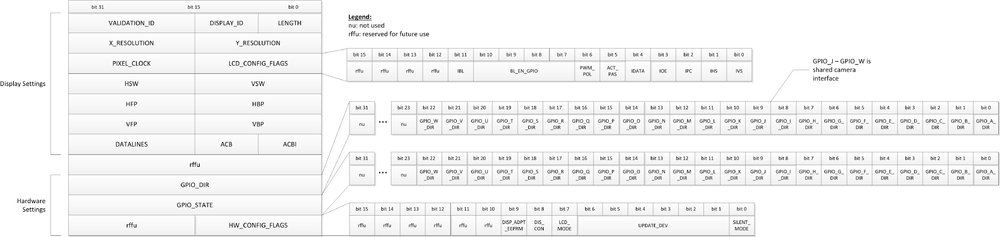
VALIDATION_ID: "DH" DISPLAY_ID: 0x00 LENGTH: 0x2c X_RESOLUTION: 800 pixel Y_RESOLUTION: 480 pixel PIXEL_CLOCK: 22200 kHz LCD_CONFIG_FLAGS: 0x3e3 HSW: 64 pixel clocks VSW: 2 line clocks HFP: 42 pixel clocks HBP: 86 pixel clocks VFP: 10 line clocks VBP: 33 line clocks DATALINES: 16 ACB: 0 ACBI: 0 GPIO_DIR: 0x01ff GPIO_STATE: 0x0000 HW_CONFIG_FLAGS: 0x001e
DHCOM settings
The Hardware settings could be configured via the DHCOM settings file in flash memory. The file contains the following settings:
(Supported from U-Boot v1.11.0.1 or higher)
Settings Block description:
| Settings Name: | Description: | Unit: |
|---|---|---|
| VALIDATION_ID | „DH“ | |
| DISPLAY_ID | unique ID of Display | |
| LENGTH | Length of the settings block | |
| X_RESOLUTION | Display x resolution | pixel |
| Y_RESOLUTION | Display y resolution | pixel |
| PIXEL_CLOCK | Pixel clock | kHz |
| LCD_CONFIG_FLAGS | LCD Configuration Register | see description |
| HSW | Horizontal synchronization pulse width | pixel clocks |
| VSW | Vertical synchronisation pulse width | line clocks |
| HFP | Horizontal front porch | pixel clocks |
| HBP | Horizontal back porch | pixel clocks |
| VFP | Vertical front porch | line clocks |
| VBP | Vertical back porch | line clocks |
| DATALINES | count of datalines | number of datalines |
| ACB | AC Bias frequency | |
| ACBI | AC Bias transitions per interrupt | |
| GPIO_DIR | DHCOM GPIO default direction register | see description |
| GPIO_STATE | DHCOM GPIO default state register | see description |
| HW_CONFIG_FLAGS | Hardware Configuration Register | see description |
- Note to PIXEL_CLOCK: Only the following pixel clock frequencies are possible:
- 33.250MHz
- 22.167MHz
- 16.625MHz
- 13.300MHz
- 11.083MHz
- 9.500MHz
- 8.312MHz
- 7.389MHz
- 6.650MHz
- ...
LCD_CONFIG_FLAGS description:
| Settings Name: | Description: | Unit: |
|---|---|---|
| IVS | Inverted Vertical Sync Pulse | 0 active high / 1 active low |
| IHS | Inverted Horizontal Sync | 0 active high / 1 active low |
| IPC | Inverted Pixel Clock | 0 Data is sampled on rising edge / 1 Data is sampled on falling edge |
| IOE | Inverted Output Enable | 0 active high / 1 active low |
| IDATA | Inverted Data | 0 active high / 1 active low |
| ACT_PAS | Active or passiv matrix display | 0 passiv / 1active |
| PWM_POL | PWM polarity | 0 low state backlight off and high state backlight on / 1 low state backlight on and high state backlight off |
| BL_EN_GPIO | Backlight enable GPIO number | 0 no backlight enable GPIO / 1 DHCOM GPIO_A / 2 DHCOM GPIO_B / … / 9 = DHCOM GPIO_I |
| IBL | Inverted Backlight Enable | 0 active high / 1 active low |
GPIO_DIR description:
| Settings Name: | Description: | Unit: |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO_A_DIR | DHCOM GPIO_A direction | 1 input / 0 output |
| GPIO_B_DIR | DHCOM GPIO_B direction | 1 input / 0 output |
| … | ||
| GPIO_I_DIR | DHCOM GPIO_I direction | 1 input / 0 output |
GPIO_STATE description:
| Settings Name: | Description: | Unit: |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO_A_STATE | DHCOM GPIO_A default state if dir = output | 1 high / 0 low |
| GPIO_B_STATE | DHCOM GPIO_B default state if dir = output | 1 high / 0 low |
| … | ||
| GPIO_I_STATE | DHCOM GPIO_I default state if dir = output | 1 high / 0 low |
HW_CONFIG_FLAGS description:
| Settings Name: | Description: | Unit: |
|---|---|---|
| SILENT_MODE | Disable Bootloader messages on FFUART | 0 enabled FFUART outputs / 1 disabled FFUART outputs |
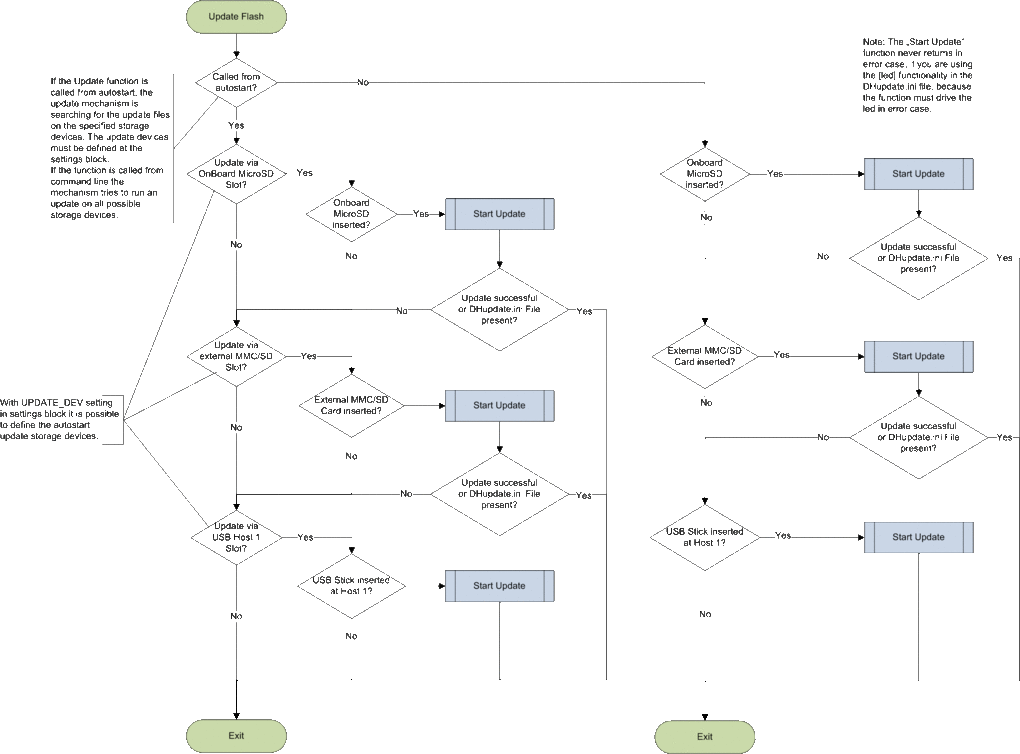
| UPDATE_DEV | Configures auto update storage devices | 0b000000 All Update Medias disabled
0bxxxxx1 Update via MicroSD Slot 0bxxxx1x Update via SD/MMC Slot 0bxxx1xx Update via USB Host 1 0bxx1xxx Update via USB OTG 0bx1xxxx Update via USB Host 2 0b1xxxxx Update via Ethernet |
| LCD_MODE | Enable Bootloader messages on LCD Display | 1 enabled / 1 disabled |
| DIS_CON | Disable Bootloader console on FFUART | 0 console enabled / 1 console disabled |
Flash Update
The follwing updates are possible with the Bootloader:
- Bootloader
- Splashimage
- Settings
- Linux image
- WinCE image
Overview
Modes
Automatically Update
- (Supported from U-Boot v1.10.0.0 or higher)
- Is called after the start of the bootloader. The functionality tries to update the flash content via the DHupdate.ini file (Please have a look at DHupdate.ini file). The update mechanism is searching for the update files on the specified storage devices. The update devices must be defined at the settings block (Please have a look at DHCOM settings). With the DHupdate.ini file you have the possibility to run more then one updates, e.g. OS image and settings block.
Command line Update
- Instruction: "update"
- (Supported from U-Boot v1.10.0.0 or higher)
- The functionality tries to update the flash content via the DHupdate.ini file. In contrast to Automatically Update the update mechanism is searching on every available storage device for the update files.
- Instruction: "update <type> [filename]"
- (Supported from U-Boot v1.5.0.0 or higher)
- The functionality doesn't use the DHupdate.ini file. It allows only one update and the update mechanism is searching on every available storage device for the update files. With the <type> parameter you have to specify the update type.
- The <type> parameter could be specified as follows:
- wince = WinCE image update + ENV update
- linux = Linux image update + ENV update
- Note: If you run linux update, u-boot searches also for an update ENV script. This script modifies the ENV for Linux. The name of the script must be the image name with the ending .env. You can also run an update without an script file. In this case u-boot only updates the image and the ENV remains unchanged.
- bootloader = Bootloader update
- Note: The ENV in Flash memory is created on the first start of u-boot. If you run a bootloader update and the ENV at the new bootloader has changed, the ENV in Flash memory remains unchanged with the bootloader update. But you could delete the ENV block in flash memory before the update, then u-boot will create the new default ENV at the next start after the bootloader update.
- splash = Bootbitmap update
- settings = Settings block update
- Note: Please have a look at DHCOM settings.
- The [filename] parameter could be used to specify a non default filename. The default filenames are:
- wince = default file names nk.gz or nk.bin
- linux = default file name uImage + default script file name uImage.env
- bootloader = default file name u-boot.bin
- splash = default file name splash.bmp
- settings = default file name settings.bin
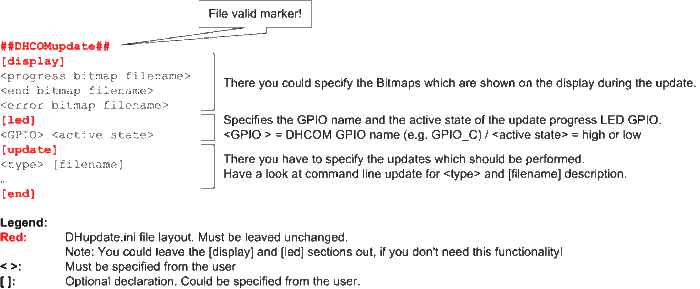
DHupdate.ini file
- The DHupdate.ini file is a text file, which describes the user specified update mechanism.
- For DHupdate.ini File Example, please have a look at the Please have a look at Download area.
- Notes:
- If you update the DHCOM settings, it is possible to use the new settings for the update progress notifications on the display, by inserting the "refresh" command to the [update] section. Example:
[update] settings 00_PV.bin refresh splash DH_800x480.bmp ... [end]
- It is necessary to use UNIX End Of Line conversion!!!
- Update progress LED description:
- The LED GPIO is activated as soon as update has started. This takes roughly 6 - 8 seconds. If the update was finished without an error, the LED GPIO is deactivated. If an error occurs during the update the LED GPIO begins blinking.
- LED error code:
- 1 LED blinking interval = DHupdate.ini File error (Wrong file content or no valid file found)
- 2 LED blinking interval = Necessary File for Update not found
- 3 LED blinking interval = Flash write or erase error
- 4 LED blinking interval = Wrong OS Image type (e.g. no WinCE *.gz or *.bin file)
- 5 LED blinking interval = Specified file not valid (e.g. linux *.env file)