COM iMX6 Bootloader U-Boot: Difference between revisions
From Wiki-DB
Jump to navigationJump to search
Ageisreiter (talk | contribs) |
Ageisreiter (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
:'''Set or show active partition''' | :'''Set or show active partition''' | ||
:{| class="wikitable" | |||
|''<code>ubi part</code>'' | |||
|} | |||
:Example: <code>mtdparts</code> | |||
=== SD/MMC Card === | === SD/MMC Card === | ||
Revision as of 14:24, 21 May 2015
FAQ
- Q: Initialization of MAC address in the bootloader?
- A: At the first start, the bootloader reads the MAC address from EEPROM, write it to eFuses and creates env variable ethaddr. The env variable ethaddr could be changed during lifetime to any other MAC address. If you like to get back the original MAC address, please remove ethaddr, save environment and restart the system. In addition to that the env variable ethaddr would be initialized again with eeprom MAC addresss.
Downloads
Enter Bootloader Console
- Connect DHCOM UART1 (FF UART) via null modem cable to the RS232 Port of your PC
- Start terminal program (e.g. Tera Term) on the Host PC with the following settings:
- Baud rate: 115200
- Data: 8 bit
- Parity: none
- Stop bits: 1 bit
- Flow control: none
- Press "del" on the Host PC during Core Module system start to enter bootloader console
U-boot console commands
SPI Flash
- SPI Flash Init
sf probe
- Example:
sf probe
- Description: Initializes the OnBoard SPI Flash
- SPI Flash Read
sf read <SDRAM address> <SPI Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example:
sf read 10000000 0 100
- Description: Copies 256Bytes from SPI Flash address 0x0 to SDRAM address 0x1000_0000
- SPI Flash Write
sf write <SDRAM address> <SPI Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example:
sf write 10000000 40000 10000
- Description: Copies 64kByte from SDRAM address 0x1000_0000 to SPI Flash address 0x4_0000
- SPI Flash Erase
sf erase <SPI Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example:
sf erase 100000 1000
- Description: Deletes SPI Flash content from address 0x10_0000 to 0x10_0FFF
- Note: The Bytes information needs to be sector size aligned!
NAND-Flash
- Read from NAND-Flash Device
nand read <SDRAM address> <NAND Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example:
nand read 80000000 400000 b40000
- Description: Copies 11,25MByte from NAND Flash address 0x40_0000 to SDRAM address 0x8000_0000
- Erase NAND-Flash blocks
nand erase <Block base address> <Bytes>
- Example:
nand erase 400000 40000
- Description: Deletes NAND Flash content from address 0x40_0000 to 0x43_FFFF
- Note: The Bytes information needs to be block size aligned!
- Write to NAND-Flash Device
nand write <SDRAM address> <NAND-Flash address> <Bytes>
- Example:
nand write 80000000 400000 b40000
- Description: Copies 11,25MByte from SDRAM address 0x8000_0000 to NAND Flash address 0x40_0000
- Note: The Bytes information needs to be page size aligned!
- Show bad NAND-Flash blocks
nand bad
- Description: Shows the bad NAND-Flash blocks.
- Show NAND-Flash content
nand dump <NAND-Flash address>
- Example:
nand dump 400000
- Description: Shows the content of the specified NAND-Flash block
UBI Filesystem
- Partition Definition
mtdparts
- Example:
mtdparts
- Description: Shows the current nand flash partitions. In case of i.MX6 one default partition set, which includes the entire flash. For linux that partition is used to create two volumes "boot" and "rootfs".
device nand0 <gpmi-nand>, # parts = 1 #: name size offset mask_flags 0: gpmi-nand 0x20000000 0x00000000 0 active partition: nand0,0 - (gpmi-nand) 0x20000000 @ 0x00000000
- Set or show active partition
ubi part
- Example:
mtdparts
SD/MMC Card
- Switch between MicroSD, SD Slot and eMMC
mmc dev <Slot number> <Partition number>
- Example:
mmc dev 0
- Description: Switch between SD/MMC Slots: 0 --> SD/MMC Slot, 1 --> MicroSD Slot, 2 --> eMMC Flash
- Note eMMC flash partition number: 0 --> User partition, 1 --> Boot partition 1, 2 --> Boot partition 2
- Initialize SD/MMC Card
mmc rescan
- Description: Initialize new inserted SD Card
- Show SD/MMC information
mmcinfo
- Description: Shows SD/MMC device information
Device: FSL_SDHC Manufacturer ID: 45 OEM: 100 Name: SEM08 Tran Speed: 52000000 Rd Block Len: 512 MMC version 4.41 High Capacity: Yes Capacity: 7.3 GiB Bus Width: 8-bit
- Write to MicroSD, SD Slot and eMMC
mmc write <SDRAM address> <block number> <block count>
- Example:
mmc write 11000000 5000 400 - Description: Write 512kByte (device block size is 512Byte) to the eMMC offset 10MByte.
- Read from MicroSD, SD Slot and eMMC
mmc read <SDRAM address> <block number> <block count>
- Example:
mmc read 11000000 5000 400 - Description: Read 512kByte (device block size is 512Byte) from the eMMC offset 10MByte.
FAT - EXT2 - EXT4 - Filesystem
- NOTE: All EXT2 commands must also be used for ext4
- Show Filesystem information
fatinfo <interface> <device>
- Example:
fatinfo mmc 1
Interface: MMC
Device 1: Vendor: Man 094150 Snr 266e068c Rev: 1.0 Prod: AF UD
Type: Removable Hard Disk
Capacity: 121.2 MB = 0.1 GB (248320 x 512)
Partition 1: Filesystem: FAT16 "NO NAME "
- List files
fatls <interface> <device> <directory>
ext2ls <interface> <device> <directory>
- Example 1:
fatls mmc 1
- Example 2:
fatls mmc 1 /folder
- Load Files from SD Card to SDRAM
fatload <interface> <device> <SDRAM address> <directory+filename>
ext2load <interface> <device> <SDRAM address> <directory+filename>
- Example 1:
fatload mmc 1 10100000 nk.gz
- Example 2:
fatload mmc 1 10100000 /folder/nk.gz
Ethernet
- Load File via TFTP to SDRAM
tftp <SDRAM address> <directory+filename>
- Example:
tftp 80100000 nk.gz
- Example TFTP Server: "Winagents TFTP Server Manager"
- Note: For TFTP download it is necessary to config the ENV variables "ipaddr" and "serverip"
- Load File via TFTP to SDRAM using DHCP
dhcp <SDRAM address> <directory+filename>
- Example:
dhcp 80100000 nk.gz
- Example TFTP Server: "Winagents TFTP Server Manager"
- Note: It is necessary to config the ENV variable "serverip" with the ip-address of your TFTP-Server
- Ping
ping <IP address>
- Example:
ping 192.168.55.32
- Read PHY register via MII interface
mii dump <PHY address> <PHY register>
- Example:
mii dump 0 0
- Remark: The standard MII registers 0-5 are supported by this command. When you are working with a DHCOM i.MX6 module only PHY address "0" is allowed.
Unzip
unzip <source address> <destination address>
- Example:
unzip 12900000 10100000
- Note: The unzip command is supporting the gzip file format.
Bitmap
- Information
bmp info <Bitmap address>
Image size : 800 x 480 Bits per pixel: 8 Compression : 0
- Display
bmp display <Bitmap SDRAM address> [x y]
- Note: It is necessary to load bitmap file to memory address with an offset of an odd multiple of +2, since the use of a four-byte alignment will cause alignment exceptions at run-time.
Memory
- Display
md[.b, .w, .l] <address> [count]
- Example:
md.b 80100000 100
- Write
mw[.b, .w, .l] <address> <value> [count]
- Example:
mw.b 80100000 aa 100
- Description: Writes the value 0xaa to the next 0x100 bytes from the address 0x8010_0000.
- Copy
cp[.b, .w, .l] <source> <destination> <count>
Show DHCOM Settings
settings
- Example:
VALIDATION_ID: "DH" DISPLAY_ID: 0x00 LENGTH: 0x2c X_RESOLUTION: 800 pixel Y_RESOLUTION: 480 pixel PIXEL_CLOCK: 22200 kHz LCD_CONFIG_FLAGS: 0x3e3 HSW: 64 pixel clocks VSW: 2 line clocks HFP: 42 pixel clocks HBP: 86 pixel clocks VFP: 10 line clocks VBP: 33 line clocks DATALINES: 16 ACB: 0 ACBI: 0 GPIO_DIR: 0x01ff GPIO_STATE: 0x0000 HW_CONFIG_FLAGS: 0x001e
I2C
- List available devices
i2c probe
Valid devices: 0 = DHCOM I2C port 1 1 = DHCOM I2C port 2 2 = i.MX6 OnBoard I2C port
- Read
i2c md <I2C address> <start address> <end address>
- Example:
i2c md 57 10 20
- Description: Reads 16 Bytes from the address 0x10 to address 0x20.
- Write
i2c mw <I2C address> <I2C register> <Value> <Bytes>
- Example:
i2c mw 57 0 aa 5
- Description: Writes 0xaa to 5 Bytes from the offset 0.
Environment
- Show ENV variables
env print
bootdelay=0 baudrate=38400 ipaddr=192.168.55.230 serverip=192.168.55.36 gatewayip=192.168.55.36 netmask=255.255.255.0 frias=5 kernel=uImage bootargs=console=ttymxc0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 nandbootwince=update;bootwince 00200000 splashimage=0x000c0000 save_ENV_to_flash=setenv ENVinFlash 1; saveenv ENVinFlash=1 ethaddr=00:04:a3:34:b6:0d ethact=FEC0 winceimagetype=nk.gz winceimagesize=00ba55ee loadaddr=00200000 bootcmd=run nandbootwince filesize=212050 Environment size: 449/262140 bytes
- Set ENV variables
env set <ENV name> <ENV value>
- Example:
env set ipaddr 192.168.55.2
- Note: If you need to edit "bootcmd" it is necessary to insert ";" between the unique commands. You can enter ";" at the command line with "\;".
- Save ENV variables
env save
- Delete ENV variable
env delete <ENV name>
- Revert to default ENV
env default -a
- Import ENV from textfile
env import -t <SDRAM address> $filesize
- Example:
fatload mmc 0 0x10000000 uEnv.txtenv import -t 0x10000000 $filesize
- Important:
- The uEnv.txt file should be in unix format. Also make sure that there is an empty line at the end of the file.
bootargs=console=ttyO0,115200n8 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 mem=128M rootwait bootcmd=mmc rescan; fatload mmc 0 0x82000000 uImage; bootm 0x82000000 uenvcmd=boot
Display and Hardware settings
DHCOM settings and Splash bitmap
- The DHCOM settings are used to setup display and special hardware parameters. For detailed description please have a look at How to create a settings.bin file.
- The DHCOM settings file and the splash bitmap are loaded via the env variables "load_settings_bin" and "load_splash" during startup from boot partition. The default content of these env variables is:
settings_bin_file=default_settings.bin
splash_file=splash.bmp
load_settings_bin=load mmc ${mmcdev}:${mmcpart} ${loadaddr} ${settings_bin_file}
load_splash=load mmc ${mmcdev}:${mmcpart} ${loadaddr} ${splash_file}
- Note: The DHCOM display settings can also be stored in external eeprom (address 0x50 / 7bit I2C address) which is connected to DHCOM I2C1 port. If eeprom is available and DISP_ADPT_EEPRM flag is set to 1, the settings from eeprom override the settings from boot partition!
- Next you can see the settings load order:
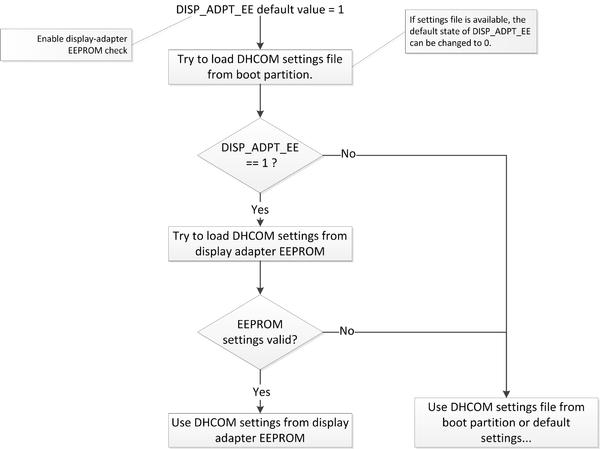
Display disabled by default
- With default u-boot configuration u-boot doesn't initialize the Display interface. This feature can be activated by deleting the "panel" environment variable. But also with deactivated display interface, the bootlaoder reads the display settings and pass the settings to the linux kernel.
panel="no_panel": Display interface is deactiveted in u-boot and backlight is powered off. panel="RGB": Default DH 4,3" display is selected. panel=deleted: u-boot initialize display by DH settings file.
Backlight enable GPIO
- If ENV variable "panel" is set to "no_panel" the backlight enable GPIO (defined via DHCOM settings file or eeprom settings) will be disabled from the bootloader during startup.
- If ENV variable "panel" is deleted, the backlight enable GPIO is activated or deactivated in relation to BL_ON flag of DHCOM settings file.
- Note: Supported by U-Boot DH VERSION v0.4.2.5 or higher for iMX6